Tensorflow - Classification
자동차의 특성을 이용하여 door를 분류/예측하는 모델링
import pandas
import numpy
데이터 준비
cars = pandas.read_csv('data/automobile.csv')
# 연속형 변수만 사용
variables = ['bore', 'city_mpg', 'compression_ratio', 'curb_weight', 'engine_size',
'horsepower', 'peak_rpm', 'city_mpg', 'price']
X = cars[variables]
y = cars['doors']
y.head()
0 four
1 four
2 four
3 four
4 two
Name: doors, dtype: object
tensorflow에서 사용할 수 있게 데이터 변환
# y를 더미 변수로 바꾼다
y_dummy = pandas.get_dummies(y).iloc[:,0]
y_dummy.head()
0 1
1 1
2 1
3 1
4 0
Name: four, dtype: uint8
# DataFrame을 행렬(matrix)로 변환
X_mat = X.as_matrix()
y_mat = y_dummy.as_matrix()
y_mat = numpy.asmatrix(y_mat).T # y를 2차원 행렬 형태로 변환
# X를 표준화(standardization)한다. 각 변수에서 평균을 빼고 표준편차로 나눈다.
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
X_std = scale(X_mat)
데이터 분할
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_std, y_mat, test_size=0.4, random_state=0)
tensorflow 초기 설정
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorlayer as tl
tf.reset_default_graph()
tl.layers.set_name_reuse(enable=True)
신경망 만들기
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 9]) # 입력 데이터. 독립변수 9개.
network = tl.layers.InputLayer(x) # 입력층
[TL] InputLayer input_layer: (?, 9)
network = tl.layers.DenseLayer(network, n_units=4, act=tf.tanh, name="hidden") # 은닉층
[TL] DenseLayer hidden: 4 tanh
network = tl.layers.DenseLayer(network, n_units=1, act=tf.sigmoid, name="output") # 출력층
[TL] DenseLayer output: 1 sigmoid
Cost
predict = network.outputs # 예측값
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # 실제 값
cost = tl.cost.binary_cross_entropy(predict, y) # cost function
data = {x: X_train, y: y_train}
Optimizer - RMSPropOptimizer
gd = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001, momentum=0.1)
train_step = gd.minimize(cost) # cost를 최소화한다
세션
session = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # = session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
predict.eval(data)[1:10, :] # 초기 예측값
array([[ 0.49829376],
[ 0.50178951],
[ 0.505391 ],
[ 0.50184959],
[ 0.50402141],
[ 0.4998126 ],
[ 0.49955413],
[ 0.50319612],
[ 0.49745575]], dtype=float32)
cost.eval(data) # 초기 비용
0.69428968
학습을 한 단계 더 진행
train_step.run(data)
cost.eval(data) # 비용이 감소한 것을 확인
0.6942789
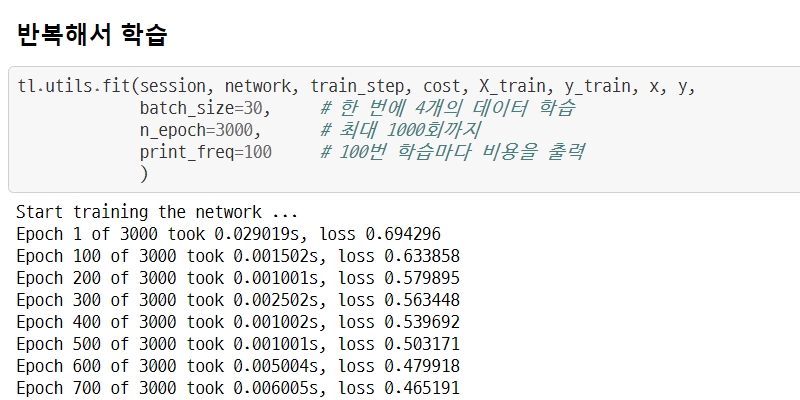
반복해서 학습
tl.utils.fit(session, network, train_step, cost, X_train, y_train, x, y,
batch_size=30, # 한 번에 4개의 데이터 학습
n_epoch=3000, # 최대 1000회까지
print_freq=100 # 100번 학습마다 비용을 출력
)
Start training the network ...
Epoch 1 of 3000 took 0.029019s, loss 0.694296
Epoch 100 of 3000 took 0.001502s, loss 0.633858
Epoch 200 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.579895
Epoch 300 of 3000 took 0.002502s, loss 0.563448
Epoch 400 of 3000 took 0.001002s, loss 0.539692
Epoch 500 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.503171
Epoch 600 of 3000 took 0.005004s, loss 0.479918
Epoch 700 of 3000 took 0.006005s, loss 0.465191
Epoch 800 of 3000 took 0.000997s, loss 0.458182
Epoch 900 of 3000 took 0.001002s, loss 0.434790
Epoch 1000 of 3000 took 0.001000s, loss 0.424537
Epoch 1100 of 3000 took 0.003004s, loss 0.393401
Epoch 1200 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.430757
Epoch 1300 of 3000 took 0.002002s, loss 0.403035
Epoch 1400 of 3000 took 0.002002s, loss 0.392969
Epoch 1500 of 3000 took 0.005003s, loss 0.416744
Epoch 1600 of 3000 took 0.001501s, loss 0.404499
Epoch 1700 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.372453
Epoch 1800 of 3000 took 0.002000s, loss 0.388540
Epoch 1900 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.375161
Epoch 2000 of 3000 took 0.002002s, loss 0.363296
Epoch 2100 of 3000 took 0.002001s, loss 0.362016
Epoch 2200 of 3000 took 0.002001s, loss 0.344575
Epoch 2300 of 3000 took 0.002008s, loss 0.341102
Epoch 2400 of 3000 took 0.000999s, loss 0.309560
Epoch 2500 of 3000 took 0.001501s, loss 0.313424
Epoch 2600 of 3000 took 0.001005s, loss 0.311816
Epoch 2700 of 3000 took 0.002002s, loss 0.314620
Epoch 2800 of 3000 took 0.002002s, loss 0.294278
Epoch 2900 of 3000 took 0.002001s, loss 0.293311
Epoch 3000 of 3000 took 0.001001s, loss 0.285992
Total training time: 5.569249s
예측
y_predict = predict.eval({x: X_test}) # test dataset으로 예측 수행
y_class = y_predict > 0.5 # 0.5와 비교
y_class[1:10]
array([[ True],
[ True],
[ True],
[ True],
[ True],
[False],
[ True],
[False],
[ True]], dtype=bool)
y_class = y_class.astype(int)
y_class[1:10]
array([[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[0],
[1],
[0],
[1]])
평가
from sklearn import metrics
metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, y_class)
array([[15, 10],
[13, 26]])
metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_class)
0.640625
metrics.precision_score(y_test, y_class, pos_label=1)
0.72222222222222221
metrics.recall_score(y_test, y_class, pos_label=1)
0.66666666666666663
metrics.f1_score(y_test, y_class, pos_label=1)
0.69333333333333336
session.close()