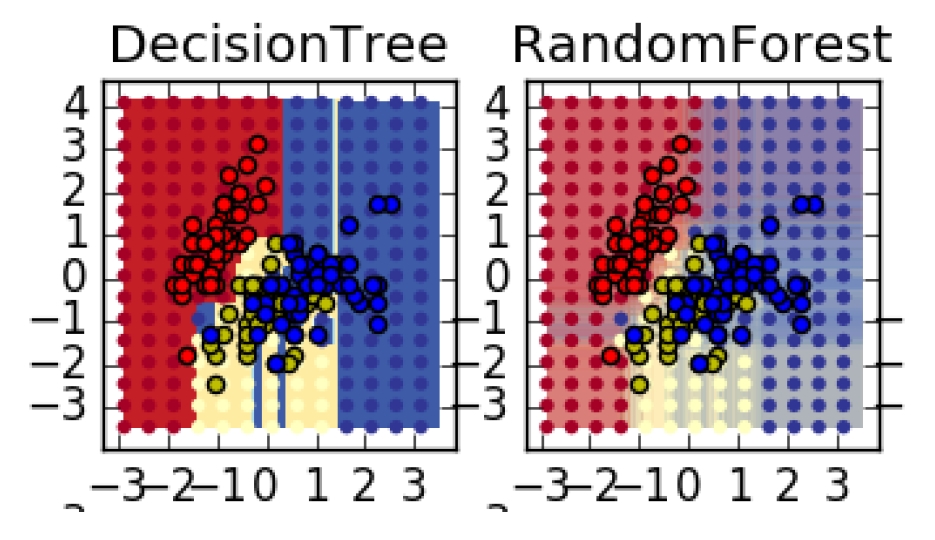
Decision Tree & Ensemble
Decision Tree, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting 모델을 이용한 예측, 범주형 변수를 dummy 변수로 변환하여 모든 변수 사용하기.
Decision Tree의 장점
- 이해하기 쉽다.
- 전처리가 단순하고 학습 속도가 빠르다.
- 다양한 종류의 변수를 다룰 수 있다.
- 모델의 시각화가 쉽다.
- 통계적 가정이 적다.
Decision Tree의 단점
- 과적합(overfitting)의 가능성이 높다.
- 결과가 불안정하다 (실행할 때마다 다른 결과 도출)
- 최적화가 어렵다.
- 학습시키기 어려운 문제들이 있다. (예, XOR 문제 등)
- 불균형 데이터에 취약하다.
앙상블 기법
- 하나의 모델은 underfitting, overfitting 될 수 있기 때문에 여러개의 모델을 만들어 다수결 또는 평균을 결과로 사용한다.
Boosting
- 모든 데이터에 동일한 가중치
- 데이터로 모형 1을 학습
- 모형 1이 틀린 데이터의 가중치 높임
- 데이터로 모형 2를 학습
- 3-4의 과정을 반복
Gradient Boosting
- 데이터로 모형 1을 학습
- 모형 1의 예측과 실제의 오차
- 위의 오차로 모형 2를 학습
- 3-4의 과정을 반복
- 실제값 = 모형 1의 예측 + 모형 1의 오차
- 모형 1의 오차 = 모형 2의 예측 + 모형 2의 오차
- 모형 2의 오차 = 모형 3의 예측 + 모형 3의 오차
- 실제값 = 모형 1의 예측 + 모형 2의 예측 + … + 아주 작은 오차
데이터 준비
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import metrics
cars = pd.read_csv('data/automobile.csv')
variables = ['bore', 'city_mpg', 'compression_ratio', 'curb_weight', 'engine_size',
'horsepower', 'peak_rpm', 'city_mpg', 'price']
X = cars[variables]
y = cars['doors']
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4)
모형 평가 출력 함수
def model_performance(y_test, y_pred):
print('confusion matrix')
print(metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
print('accuracy : {}'.format(metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)))
print('precision : {}'.format(metrics.precision_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label='four')))
print('recall : {}'.format(metrics.recall_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label='four')))
print('F1 : {}'.format(metrics.f1_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label='four')))
1. Decision Tree
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier()
tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_split=1e-07, min_samples_leaf=1,
min_samples_split=2, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
presort=False, random_state=None, splitter='best')
y_pred = tree.predict(X_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred)
confusion matrix
[[29 12]
[ 7 16]]
accuracy : 0.703125
precision : 0.8055555555555556
recall : 0.7073170731707317
F1 : 0.7532467532467532
# 모델에서 각 변수의 중요도
varDic = {'var':variables, 'importance':tree.feature_importances_}
importance = pd.DataFrame(varDic)
importance
| importance | var | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.053534 | bore |
| 1 | 0.108305 | city_mpg |
| 2 | 0.000000 | compression_ratio |
| 3 | 0.190495 | curb_weight |
| 4 | 0.275549 | engine_size |
| 5 | 0.048502 | horsepower |
| 6 | 0.021454 | peak_rpm |
| 7 | 0.036779 | city_mpg |
| 8 | 0.265382 | price |
2. Random Forest
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=0)
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_split=1e-07, min_samples_leaf=1,
min_samples_split=2, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
n_estimators=10, n_jobs=1, oob_score=False, random_state=0,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
y_pred_rf = rf.predict(X_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred_rf)
confusion matrix
[[31 10]
[12 11]]
accuracy : 0.65625
precision : 0.7209302325581395
recall : 0.7560975609756098
F1 : 0.7380952380952381
3. Gradient Boosting Tree
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=10, random_state=0)
gb.fit(X_train, y_train)
GradientBoostingClassifier(criterion='friedman_mse', init=None,
learning_rate=0.1, loss='deviance', max_depth=3,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_split=1e-07, min_samples_leaf=1,
min_samples_split=2, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
n_estimators=10, presort='auto', random_state=0,
subsample=1.0, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
y_pred_gb = gb.predict(X_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred_gb)
confusion matrix
[[40 1]
[15 8]]
accuracy : 0.75
precision : 0.7272727272727273
recall : 0.975609756097561
F1 : 0.8333333333333334
범주형 변수를 dummy 변수로 변환하여 모든 변수 사용
# target인 door를 제외한 모든 범주형 변수
cate_var = cars.columns[cars.dtypes == 'object'].difference(['doors'])
cate_var
Index(['aspiration', 'body', 'cylinders', 'engine_location', 'engine_type',
'fuel', 'fuel_system', 'maker', 'wheels'],
dtype='object')
# 범주형 변수를 dummy 변수로 변환
dummyVar = pd.get_dummies(cars[cate_var])
X_all = pd.concat([X, dummyVar], axis=1) # 연속형 변수와 범주형 변수 합치기
X_all.head()
| bore | city_mpg | compression_ratio | curb_weight | engine_size | horsepower | peak_rpm | city_mpg | price | aspiration_std | ... | maker_plymouth | maker_porsche | maker_saab | maker_subaru | maker_toyota | maker_volkswagen | maker_volvo | wheels_4wd | wheels_fwd | wheels_rwd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.19 | 24 | 10.0 | 2337 | 109 | 102 | 5500 | 24 | 13950 | 1 | ... | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 3.19 | 18 | 8.0 | 2824 | 136 | 115 | 5500 | 18 | 17450 | 1 | ... | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 3.19 | 19 | 8.5 | 2844 | 136 | 110 | 5500 | 19 | 17710 | 1 | ... | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 3.13 | 17 | 8.3 | 3086 | 131 | 140 | 5500 | 17 | 23875 | 0 | ... | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 3.50 | 23 | 8.8 | 2395 | 108 | 101 | 5800 | 23 | 16430 | 1 | ... | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
5 rows × 56 columns
X_all_train, X_all_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_all, y, test_size=0.4)
SVC
from sklearn.svm import SVC
model = SVC(kernel='rbf')
model.fit(X_all_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_all_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred)
confusion matrix
[[41 0]
[23 0]]
accuracy : 0.640625
precision : 0.640625
recall : 1.0
F1 : 0.780952380952381
DecisionTree
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(X_all_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_all_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred)
confusion matrix
[[33 8]
[11 12]]
accuracy : 0.703125
precision : 0.75
recall : 0.8048780487804879
F1 : 0.7764705882352942
RandomForest
model = RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(X_all_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_all_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred)
confusion matrix
[[36 5]
[ 9 14]]
accuracy : 0.78125
precision : 0.8
recall : 0.8780487804878049
F1 : 0.8372093023255814
GradientBoosting
model = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
model.fit(X_all_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_all_test)
model_performance(y_test, y_pred)
confusion matrix
[[38 3]
[ 6 17]]
accuracy : 0.859375
precision : 0.8636363636363636
recall : 0.926829268292683
F1 : 0.8941176470588236