Tensorflow Name Scope
Name Scope의 개념 및 적용. tensorflow graph의 변수값 변화 추이를 tensorboard 플롯을 통해 확인하기.
Tensorflow - name scope
복잡한 그래프를 다루기 위해 텐서플로는 name scope를 통해 여러 오퍼레이션을 block 단위로 묶을 수 있다. 이를 통해 그래프 시각화를 단순화할 수 있다.
name scope 예제 1
import tensorflow as tf
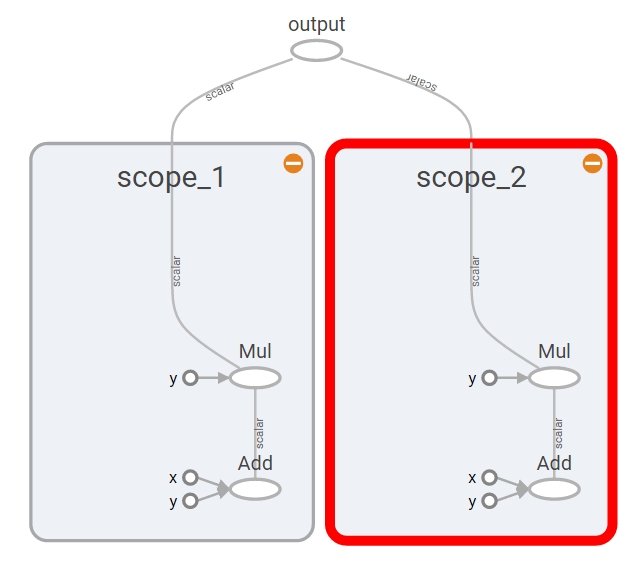
with tf.name_scope("scope_1"):
a = tf.add(1, 2)
b = tf.multiply(a, 3)
with tf.name_scope("scope_2"):
x = tf.add(7, 8)
y = tf.multiply(x, 9)
o = tf.add(b, y, name="output")
sess = tf.Session()
# tensorboard 시각화
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('c:\Github\output01', graph=sess.graph)
writer.close()
(터미널) tensorboard –logdir=”c:\Github\output01”
(브라우저) http://localhost:6006
sess.close()
name scope 예제 2 - 중첩
graph = tf.get_default_graph() # 명시적으로 그래프 객체 생성
with graph.as_default():
input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[], name="input_1")
input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[], name="input_2")
const = tf.constant(9, dtype=tf.float32, name="static_value")
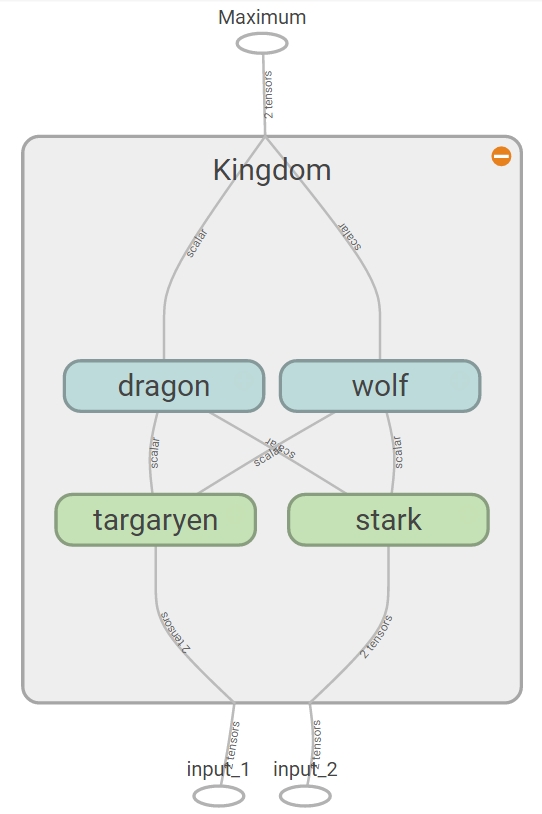
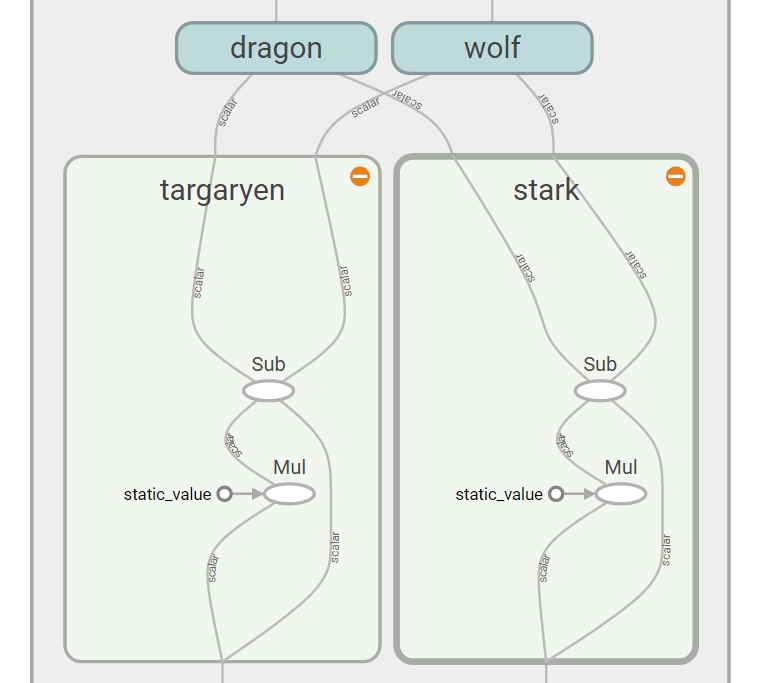
with tf.name_scope("Kingdom"):
with tf.name_scope("targaryen"):
t_mul = tf.multiply(input1, const)
t_out = tf.subtract(t_mul, input1)
with tf.name_scope("stark"):
s_mul = tf.multiply(input2, const)
s_out = tf.subtract(s_mul, input2)
with tf.name_scope("dragon"):
d_div = tf.div(t_out, s_out)
d_out = tf.add(d_div, const)
with tf.name_scope("wolf"):
w_div = tf.div(s_out, t_out)
w_out = tf.add(w_div, const)
out = tf.maximum(d_out, w_out)
sess = tf.Session()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('c:\Github\output02', graph)
writer.close()
sess.close()
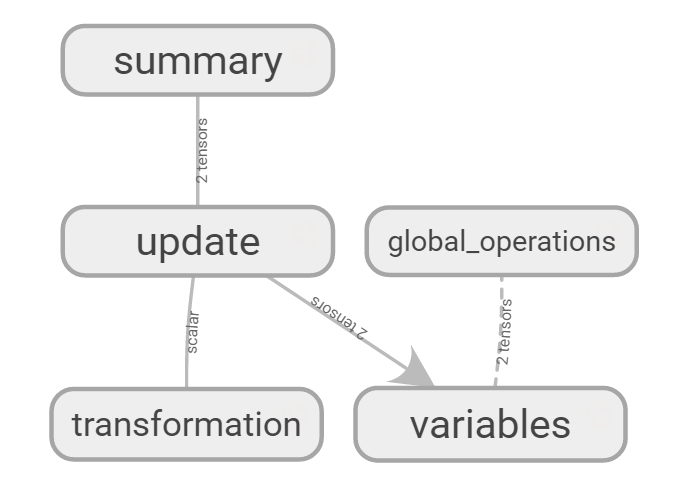
name scope 예제 3
import tensorflow as tf
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
with graph.as_default():
with tf.name_scope("variables"):
# 그래프가 실행되는 횟수 추적
global_step = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.int32, trainable=False)
# 출력값의 합계를 추적
total_output = tf.Variable(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, trainable=False)
# 입력, 연산, 출력
with tf.name_scope("transformation"):
with tf.name_scope("input"):
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None], name="input_placeholder")
with tf.name_scope("middle_layer"):
m_prod = tf.reduce_prod(a, name="product_m")
m_sum = tf.reduce_sum(a, name="sum_m")
with tf.name_scope("output"):
output = tf.add(m_prod, m_sum, name="output")
# 전역변수 업데이트
with tf.name_scope("update"):
update_total = total_output.assign_add(output) # 최종 출력값을 누적
increment_step = global_step.assign_add(1) # 그래프 수행 횟수 증가
# tensorboard에서 보여주기 위해 summary
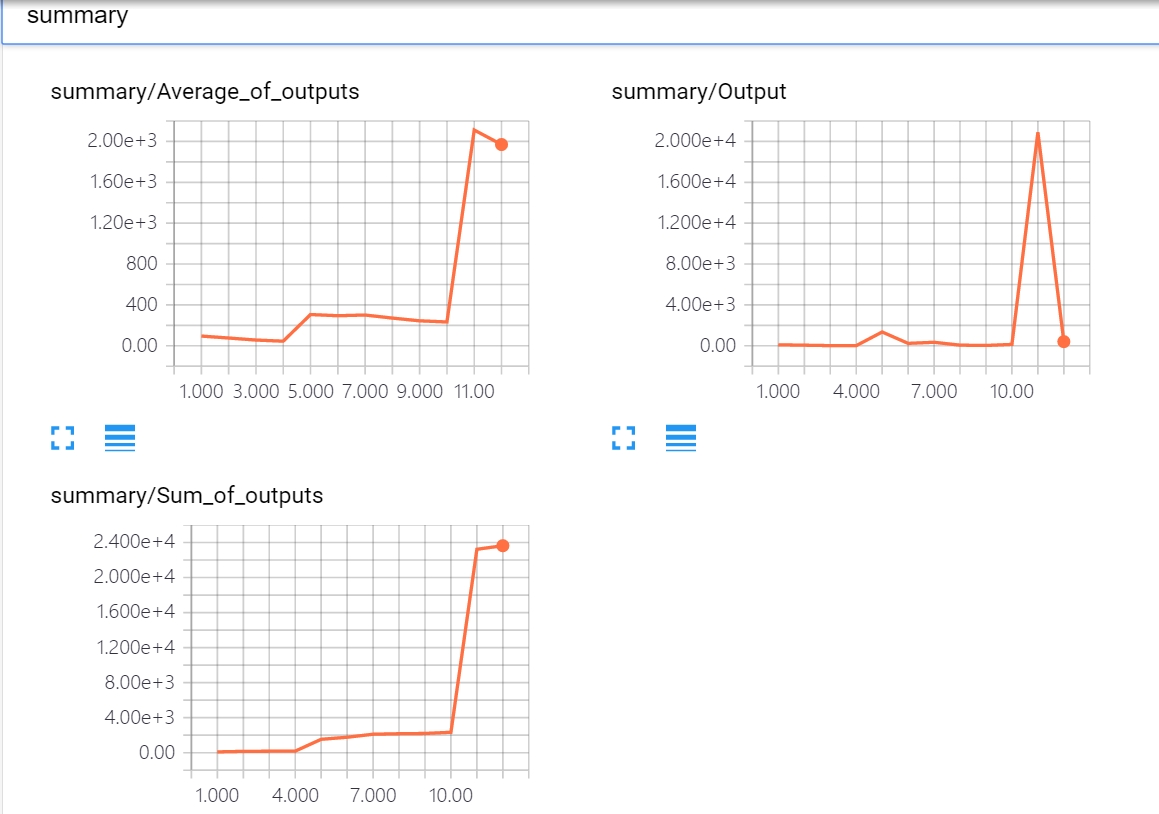
with tf.name_scope("summary"):
avg = tf.div(update_total, tf.cast(increment_step, tf.float32), name="average")
tf.summary.scalar('Output', output)
tf.summary.scalar('Sum_of_outputs', update_total)
tf.summary.scalar('Average_of_outputs', avg)
with tf.name_scope("global_operations"):
merged_summaries = tf.summary.merge_all() # merge all summaries
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # initialization
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('c:\Github\output03', graph)
# 그래프를 실행하기 위한 함수
def run_graph(input_tensor):
feed_dict = {a: input_tensor} # 변수 재설정. np.array(input_tensor, dtype=np.float32)
# 세션 실행 후 결과값 저장
_, step, summary = sess.run([output, increment_step, merged_summaries], feed_dict=feed_dict)
# 텐서보드가 그래프 그리도록 값을 추가
writer.add_summary(summary, global_step=step)
# 실제 값으로 그래프 실행
run_graph([2,8,5])
run_graph([3,1,3,5])
run_graph([8])
run_graph([1,2,3])
run_graph([7,9,3,7])
run_graph([8,3,9])
run_graph([6,6,3,3])
run_graph([6,4,2,1])
run_graph([2,9])
run_graph([4,5,6])
run_graph([10,33,63])
run_graph([5,7,11])
writer.flush() # write the summaries to disk
writer.close()
sess.close()
(터미널) tensorboard –logdir=”c:\Github\output03”