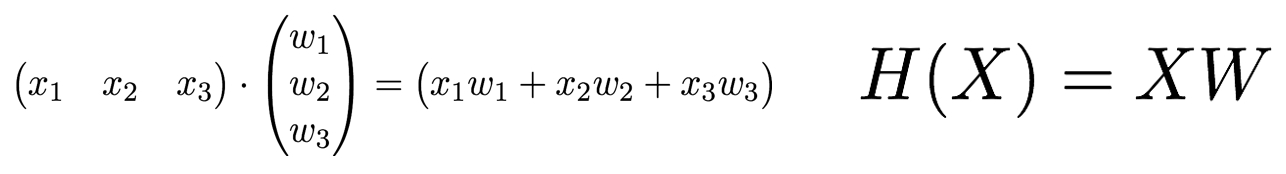Tensorflow 호텔 신규지점 마진 예측
[딥러닝] 다변량 선형회귀를 이용한 호텔 신규지점 마진 예측, 성적 예측
Hypothesis with Matrix
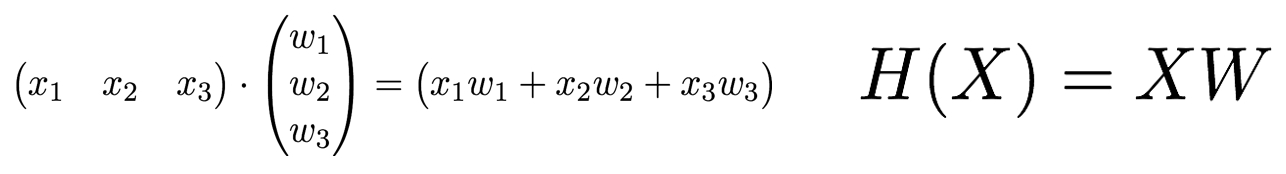
3과목의 점수로 최종 점수 예측
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# import data from file
data = np.loadtxt('data/test-score.csv', delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
data.shape
(25, 4)
# 3 features
x_data = data[:, 0:-1] # 1 ~ 3 번째 컬럼
y_data = data[:, [-1]] # 마지막 컬럼
# shape 설정
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 3]) # input feature 수 : [n, 3] * [3,1] = [n, 1]
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1]) # output feature 수
# variable 의 수 = 3
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
# 행렬 곱
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
# modeling
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-5)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
# run graph
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 학습
for step in range(7001):
cost_val, hy_val, _ = sess.run([cost, hypothesis, train], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, "Cost: ", cost_val)
if step == 7000:
print("Prediction:\n", hy_val)
0 Cost: 166097.0
1000 Cost: 15.8229
2000 Cost: 11.9062
3000 Cost: 9.59181
4000 Cost: 8.21307
5000 Cost: 7.38697
6000 Cost: 6.88998
7000 Cost: 6.59009
Prediction:
[[ 152.36933899]
[ 185.24554443]
[ 181.32817078]
[ 198.60925293]
[ 140.90942383]
[ 105.94801331]
[ 149.80859375]
[ 112.57711029]
[ 175.03233337]
[ 164.85656738]
[ 143.80343628]
[ 143.18138123]
[ 186.19641113]
[ 153.31900024]
[ 150.94363403]
[ 188.87088013]
[ 145.30027771]
[ 179.97668457]
[ 177.00708008]
[ 158.37261963]
[ 175.54580688]
[ 174.77584839]
[ 166.86877441]
[ 150.97592163]
[ 191.10281372]]
# 나와 친구의 최종 점수 예측
sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X: [[100, 70, 100], [90, 100, 80]]})
array([[ 188.35801697],
[ 175.17378235]], dtype=float32)
호텔체인 신규 지점의 마진 예측
# import data
data = np.loadtxt('data/laquinta.csv', delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
data.shape
(100, 7)
features
- Number : 3 마일 내에 있는 모텔 또는 호텔의 객실 수 (1000개)
- Nearest : 가장 가까운 모텔 또는 호텔과의 거리 (마일)
- OfficeSpace : 주변 지역에 있는 사무실의 규모 (1000 평방 피트)
- Enrollment : 근처 대학의 학생수 (1000 명)
- Income : 주변 지역의 중위 소득 ($1000)
- Distance : 시내 중심까지의 거리
x_data = data[:, 0:-1]
y_data = data[:, [-1]]
x_data.shape
(100, 6)
x_data[:,0] = x_data[:,0] / 1000
x_data[:,2] = x_data[:,2] / 100
x_data[0,:]
array([ 3.20300007, 4.19999981, 5.48999977, 8. ,
37. , 2.70000005], dtype=float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 6])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([6, 1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-5)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(30001):
cost_val, hy_val, _ = sess.run([cost, hypothesis, train], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 3000 == 0:
print(step, "Cost: ", cost_val)
if step == 30000:
print("Prediction:\n", hy_val[:30])
0 Cost: 353.289
3000 Cost: 64.4129
6000 Cost: 56.8195
9000 Cost: 52.2762
12000 Cost: 49.138
15000 Cost: 46.8647
18000 Cost: 45.1828
21000 Cost: 43.9219
24000 Cost: 42.9658
27000 Cost: 42.2325
30000 Cost: 41.663
Prediction:
[[ 44.76677704]
[ 44.83603287]
[ 42.98330688]
[ 45.31852341]
[ 52.92823029]
[ 45.70767212]
[ 44.85763168]
[ 47.08715439]
[ 48.97818756]
[ 54.33695221]
[ 46.06202698]
[ 33.66534805]
[ 40.40279388]
[ 52.52919006]
[ 36.8804512 ]
[ 42.9991684 ]
[ 48.62209702]
[ 39.7893219 ]
[ 46.79165649]
[ 46.04627991]
[ 40.36611557]
[ 43.29184723]
[ 48.91107178]
[ 55.18282318]
[ 50.87582397]
[ 44.81761169]
[ 47.78472519]
[ 43.96390533]
[ 34.89593124]
[ 48.3162117 ]]
# 신규 지점의 마진 예측
# 경쟁사 객실수 : 3815, 가까운 경쟁사 거리 : 0.9, 주변 사무실 : 4.76, 주변 대학생 수 : 24500, 중위 소득 : 35,000, 시내까지 거리 : 11.2
sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X: [[3.815, 0.9, 4.76, 24.5, 35.0, 11.2]]})
array([[ 45.95544815]], dtype=float32)
데이터 파일 여러 개를 Queue로 불러오기
# filename queue
files = ['data/test-score.csv', 'data/test-score02.csv']
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files, shuffle=False, name='filename_queue')
# reader
reader = tf.TextLineReader()
key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
# Default values
record_defaults = [[0.], [0.], [0.], [0.]] # 3 개의 컬럼 + y
data = tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults=record_defaults)
# collect batches of csv
train_x_batch, train_y_batch = tf.train.batch([data[0:-1], data[-1:]], batch_size=20)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 3])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-5)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Start populating the filename queue.
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
# 학습
for step in range(5001):
x_batch, y_batch = sess.run([train_x_batch, train_y_batch])
cost_val, hy_val, _ = sess.run([cost, hypothesis, train], feed_dict={X: x_batch, Y: y_batch})
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, "Cost: ", cost_val)
if step == 5000:
print("Prediction:\n", hy_val)
0 Cost: 20920.5
1000 Cost: 30.1588
2000 Cost: 19.7607
3000 Cost: 14.552
4000 Cost: 11.8061
5000 Cost: 10.2829
Prediction:
[[ 151.59170532]
[ 186.13923645]
[ 181.2706604 ]
[ 197.42167664]
[ 143.16911316]
[ 106.47771454]
[ 147.0309906 ]
[ 107.73338318]
[ 175.11833191]
[ 162.87550354]
[ 142.83317566]
[ 142.72502136]
[ 187.21566772]
[ 155.9540863 ]
[ 148.33409119]
[ 188.58197021]
[ 149.74754333]
[ 175.33354187]
[ 177.87763977]
[ 158.83981323]]
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
# 나와 친구의 최종 점수 예측
sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X: [[100, 70, 100], [90, 100, 80]]})
array([[ 191.31782532],
[ 178.37687683]], dtype=float32)