Python Basics 3
Iterator, Generator, List comprehensions, generators for streaming data & large files
Iterating
import pandas as pd
flist = ['targaryen', 'stark', 'baratheon', 'tully', 'lannister', 'tyrell', 'martell']
alist = ['dragon','wolf','deer','fish','lion','rose','sun']
nlist = ['대너리스','에다드','로버트','브린덴','제이미','로라스','도란'];
for item in flist:
print(item)
targaryen
stark
baratheon
tully
lannister
tyrell
martell
# make iterator from list
superspeed = iter(flist)
print(next(superspeed))
print(next(superspeed))
print(next(superspeed))
targaryen
stark
baratheon
small_value = iter(range(3))
print(next(small_value))
print(next(small_value))
print(next(small_value))
0
1
2
googol = iter(range(10 ** 1000)) # big number - may not work
print(next(googol))
print(next(googol))
0
1
enumerate
enumlist = list(enumerate(flist)) # list of tuple
print(enumlist)
[(0, 'targaryen'), (1, 'stark'), (2, 'baratheon'), (3, 'tully'), (4, 'lannister'), (5, 'tyrell'), (6, 'martell')]
for index1, value1 in enumlist: # unpack tuple
print(index1, value1)
0 targaryen
1 stark
2 baratheon
3 tully
4 lannister
5 tyrell
6 martell
for index2, value2 in enumerate(flist, start = 1): # Change the start index
print(index2, value2)
1 targaryen
2 stark
3 baratheon
4 tully
5 lannister
6 tyrell
7 martell
zip
m_data = list(zip(nlist, flist, alist))
print(m_data)
[('대너리스', 'targaryen', 'dragon'), ('에다드', 'stark', 'wolf'), ('로버트', 'baratheon', 'deer'), ('브린덴', 'tully', 'fish'), ('제이미', 'lannister', 'lion'), ('로라스', 'tyrell', 'rose'), ('도란', 'martell', 'sun')]
m_zip = zip(nlist, flist, alist) # create zip object
print(m_zip)
for value1, value2, value3 in m_zip: # unzip
print(value1, value2, value3)
<zip object at 0x0000017E86695F48>
대너리스 targaryen dragon
에다드 stark wolf
로버트 baratheon deer
브린덴 tully fish
제이미 lannister lion
로라스 tyrell rose
도란 martell sun
# unzip (*)
m_zip = zip(nlist, flist, alist)
print(*m_zip)
('대너리스', 'targaryen', 'dragon') ('에다드', 'stark', 'wolf') ('로버트', 'baratheon', 'deer') ('브린덴', 'tully', 'fish') ('제이미', 'lannister', 'lion') ('로라스', 'tyrell', 'rose') ('도란', 'martell', 'sun')
m_zip = zip(nlist, flist, alist)
result1, result2, result3 = zip(*m_zip) # unzip to tuple
print(result2)
print(flist)
print(result2 == flist) # Check if unpacked tuples are equivalent to original tuples
('targaryen', 'stark', 'baratheon', 'tully', 'lannister', 'tyrell', 'martell')
['targaryen', 'stark', 'baratheon', 'tully', 'lannister', 'tyrell', 'martell']
False
iteration by chunk
counts_dict = {}
# Iterate over the file chunk by chunk
for chunk in pd.read_csv('data/tweets.csv', chunksize = 10):
# Iterate over the column in dataframe
for entry in chunk.lang:
if entry in counts_dict.keys():
counts_dict[entry] += 1
else:
counts_dict[entry] = 1
print(counts_dict)
{'kr': 12, 'jp': 36, 'ru': 6, 'en': 222, 'et': 24}
# count entry function with chunksize
def count_entries(csv_file, c_size, colname):
"""Return a dictionary with counts of ccurrences as value for each key."""
counts_dict = {}
for chunk in pd.read_csv(csv_file, chunksize=c_size):
for entry in chunk[colname]:
if entry in counts_dict.keys():
counts_dict[entry] += 1
else:
counts_dict[entry] = 1
return counts_dict
result_counts = count_entries('data/tweets.csv', 10, 'lang')
print(result_counts)
{'kr': 12, 'jp': 36, 'ru': 6, 'en': 222, 'et': 24}
List comprehensions
squares = [i**2 for i in range(10)]
# Create a 5 x 5 matrix using a list of lists
matrix = [[col for col in range(5)] for row in range(5)]
for row in matrix:
print(row)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
# conditionals in comprehensions
new_fellowship = [member for member in flist if len(member) >= 7]
print(new_fellowship)
['targaryen', 'baratheon', 'lannister', 'martell']
new_fellowship = [member if len(member) >= 7 else '' for member in flist]
print(new_fellowship)
['targaryen', '', 'baratheon', '', 'lannister', '', 'martell']
# tweet_clock_time = [entry[11:19] for entry in tweet_time if entry[17:19] == '19']
# Dict comprehensions
new_fellowship = {member:len(member) for member in flist}
print(new_fellowship)
{'tully': 5, 'tyrell': 6, 'martell': 7, 'targaryen': 9, 'stark': 5, 'baratheon': 9, 'lannister': 9}
Generator : Lazy evaluation
# Create a generator object
lengths = (len(person) for person in flist)
for value in lengths:
print(value)
9
5
9
5
9
6
7
# [num for num in range(10**10000000)] -- 대용량 데이터일 경우 문제 발생
# (num for num in range(10**100000)) # generator 객체 만든 후 요청시에만 처리되기 때문에 대용량 데이터 처리시 안전.
Dictionary by zip
# 2개의 list 를 dictionary로 만드는 함수
def lists2dict(list1, list2):
"""list1 provides the keys and list2 provides the values."""
zipped_lists = zip(list1, list2)
rs_dict = dict(zipped_lists)
return rs_dict
fa_dict = lists2dict(alist, flist)
fa_dict
{'deer': 'baratheon',
'dragon': 'targaryen',
'fish': 'tully',
'lion': 'lannister',
'rose': 'tyrell',
'sun': 'martell',
'wolf': 'stark'}
list + list > dictionary > dataframe
feature_names = ['familyname','firstname','crest']
row_list = []
m_zip = zip(flist, nlist, alist)
for value1, value2, value3 in m_zip:
item = (value1, value2, value3)
row_list.append(item)
row_list
[('targaryen', '대너리스', 'dragon'),
('stark', '에다드', 'wolf'),
('baratheon', '로버트', 'deer'),
('tully', '브린덴', 'fish'),
('lannister', '제이미', 'lion'),
('tyrell', '로라스', 'rose'),
('martell', '도란', 'sun')]
list_of_dicts = [lists2dict(feature_names, sublist) for sublist in row_list]
list_of_dicts
[{'crest': 'dragon', 'familyname': 'targaryen', 'firstname': '대너리스'},
{'crest': 'wolf', 'familyname': 'stark', 'firstname': '에다드'},
{'crest': 'deer', 'familyname': 'baratheon', 'firstname': '로버트'},
{'crest': 'fish', 'familyname': 'tully', 'firstname': '브린덴'},
{'crest': 'lion', 'familyname': 'lannister', 'firstname': '제이미'},
{'crest': 'rose', 'familyname': 'tyrell', 'firstname': '로라스'},
{'crest': 'sun', 'familyname': 'martell', 'firstname': '도란'}]
df_game = pd.DataFrame(list_of_dicts)
df_game
| crest | familyname | firstname | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | dragon | targaryen | 대너리스 |
| 1 | wolf | stark | 에다드 |
| 2 | deer | baratheon | 로버트 |
| 3 | fish | tully | 브린덴 |
| 4 | lion | lannister | 제이미 |
| 5 | rose | tyrell | 로라스 |
| 6 | sun | martell | 도란 |
Python generators for streaming data
- Use a generator to load a file line by line.
- Works on streaming data.
- Read and process the file until all lines are exhausted.
일반적인 방법
# Open a connection to the file
with open('data/movielens_ratings.csv') as file:
file.readline() # Skip the column names
counts_dict = {}
# Process only the first 1000 rows
for j in range(1000):
# Split the current line into a list: line
line = file.readline().split(',')
# Get the value for the first column: userid
first_col = line[0]
# userId 별 평점 부여 횟수
if first_col in counts_dict.keys():
counts_dict[first_col] += 1
else:
counts_dict[first_col] = 1
print(counts_dict)
{'3': 51, '14': 20, '9': 45, '8': 116, '10': 46, '12': 61, '1': 20, '15': 38, '4': 204, '5': 100, '2': 76, '13': 53, '7': 88, '11': 38, '6': 44}
Large file인 경우 처리방법
def read_large_file(file_object):
"""A generator function to read a large file lazily."""
# Loop indefinitely until the end of the file
while True:
data = file_object.readline()
# Break if this is the end of the file
if not data:
break
# Yield the line of data
yield data
counts_dict = {}
counts = 0
with open('data/movielens_ratings.csv') as file:
# Iterate over the generator from read_large_file()
for line in read_large_file(file):
counts += 1
if counts >= 1000:
break
row = line.split(',')
first_col = row[0]
if first_col in counts_dict.keys():
counts_dict[first_col] += 1
else:
counts_dict[first_col] = 1
print(counts_dict)
{'3': 51, '14': 20, 'userId': 1, '9': 45, '8': 116, '10': 46, '12': 61, '1': 20, '15': 36, '4': 204, '5': 100, '2': 76, '13': 53, '7': 88, '11': 38, '6': 44}
iterator to load data in chunks
file_reader = pd.read_csv('data/movielens_ratings.csv', chunksize=1000)
# Get the first dataframe chunk
df_reader = next(file_reader)
df_reader.head()
| userId | movieId | rating | timestamp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 31 | 2.5 | 1260759144 |
| 1 | 1 | 1029 | 3.0 | 1260759179 |
| 2 | 1 | 1061 | 3.0 | 1260759182 |
| 3 | 1 | 1129 | 2.0 | 1260759185 |
| 4 | 1 | 1172 | 4.0 | 1260759205 |
iterator to load data in chunks 2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# Initialize reader object: urb_pop_reader
urb_pop_reader = pd.read_csv('data/ind_pop_data.csv', chunksize=1000)
# Get the first dataframe chunk: df_urb_pop
df_urb_pop = next(urb_pop_reader)
# Check out specific country: df_pop_ceb
df_pop_ceb = df_urb_pop[df_urb_pop['CountryCode'] == 'AFG']
df_pop_ceb.head()
| CountryName | CountryCode | Year | TotalPop | UrbanPopRatio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1960 | 8990000.0 | 8.22 |
| 1 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1961 | 9160000.0 | 8.51 |
| 2 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1962 | 9340000.0 | 8.81 |
| 3 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1963 | 9530000.0 | 9.11 |
| 4 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1964 | 9730000.0 | 9.43 |
# Zip dataframe columns of interest: pops
pops = zip(df_pop_ceb['TotalPop'], df_pop_ceb['UrbanPopRatio'])
# Turn zip object into list: pops_list
pops_list = list(pops)
# Use list comprehension to create new dataframe column 'Total Urban Population'
df_pop_ceb['TotalUrbanPopulation'] = [int(tup[0] * tup[1]) for tup in pops_list]
df_pop_ceb.head()
C:\Python\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\ipykernel\__main__.py:2: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy
from ipykernel import kernelapp as app
| CountryName | CountryCode | Year | TotalPop | UrbanPopRatio | TotalUrbanPopulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1960 | 8990000.0 | 8.22 | 73897800 |
| 1 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1961 | 9160000.0 | 8.51 | 77951600 |
| 2 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1962 | 9340000.0 | 8.81 | 82285400 |
| 3 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1963 | 9530000.0 | 9.11 | 86818300 |
| 4 | Afghanistan | AFG | 1964 | 9730000.0 | 9.43 | 91753900 |
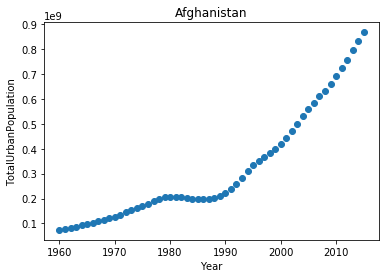
# Plot urban population data
plt.scatter(df_pop_ceb['Year'], df_pop_ceb['TotalUrbanPopulation'])
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('TotalUrbanPopulation')
plt.title('Afghanistan')
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x17e880b7a58>